|
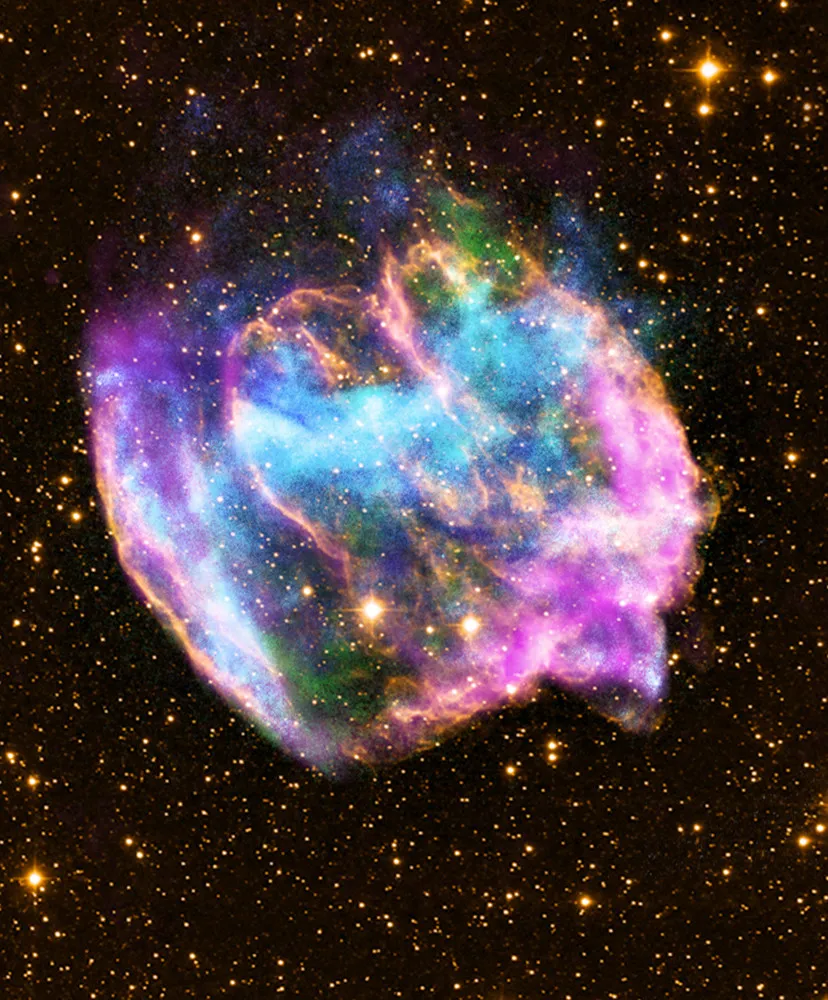
This NASA Chandra X-Ray Observatory image shows a highly distorted supernova remnant that may contain the most recent black hole formed in the Milky Way galaxy. The composite image combines X-rays from Chandra (blue and green), radio data from the Very Large Array (pink), and infrared data from the Palomar Observatory (yellow). Most supernova explosions that destroy massive stars are generally symmetrical. In the W49B supernova, however, it appears that the material near its poles was ejected at much higher speeds than that at its equator. There is also evidence that the explosion that produced W49B left behind a black hole and not a neutron star like most other supernovas. (Photo by L. Lopez/MIT/CXC/NASA via AFP Photo)
|