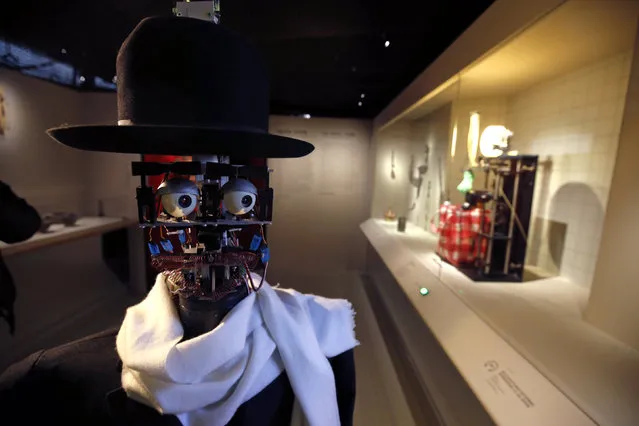
The Berenson robot strolls among visitors during the exhibition “Persona : Oddly Human” at the Quai Branly museum in Paris, France, February 23, 2016. The Berenson robot, developed in France in 2011, is the brainchild of anthropologist Denis Vidal and robotics engineer Philippe Gaussier. Its programming allows it to record reactions of museum visitors to certain pieces of art and then use the data to develop its own unique taste, which allows “Berenson” to judge whether or not it likes a certain work of art within an exhibition. (Photo by Philippe Wojazer/Reuters)