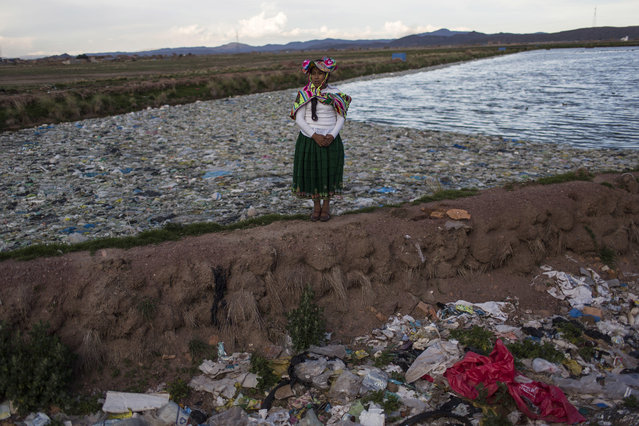
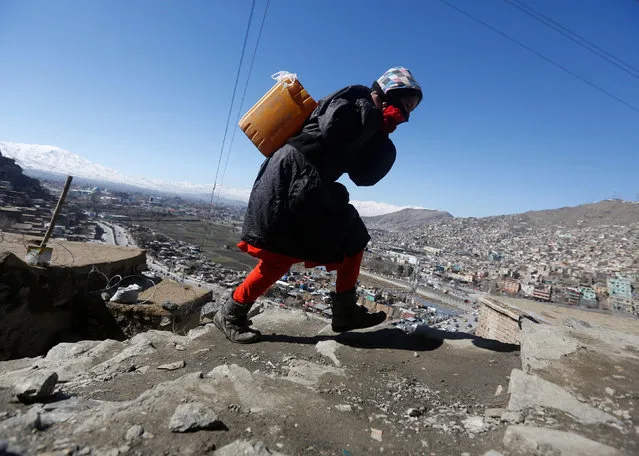
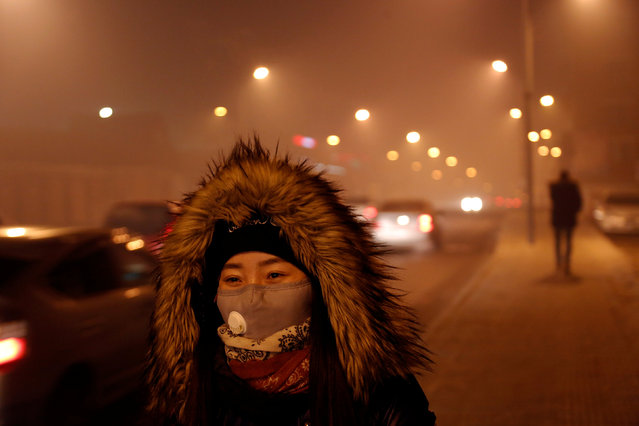
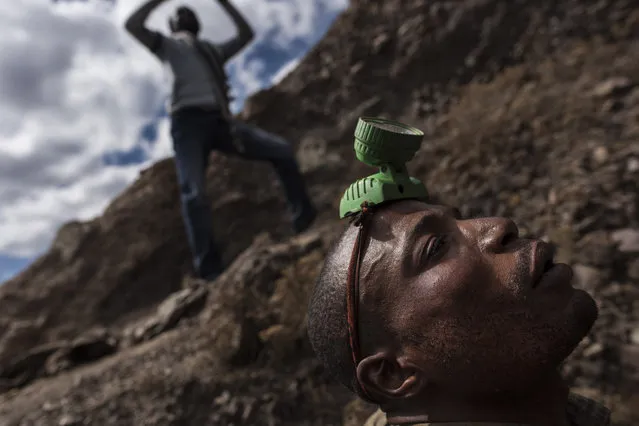
In this February 1, 2017 photo, environmental activist Maruja Inquilla poses for a photo next to a Municipal waste treatment plant with water that flows into Lake Titicaca, in Juliaca, in the Puno region of Peru. “If the frogs could talk they would say, This is killing me”," said Inquilla, who recently showed up at the Puno governor's house carrying plastic bags filled with hundreds of dead frogs in protest. (Photo by Rodrigo Abd/AP Photo)
04 Mar 2017 00:02:00,post received
0 comments