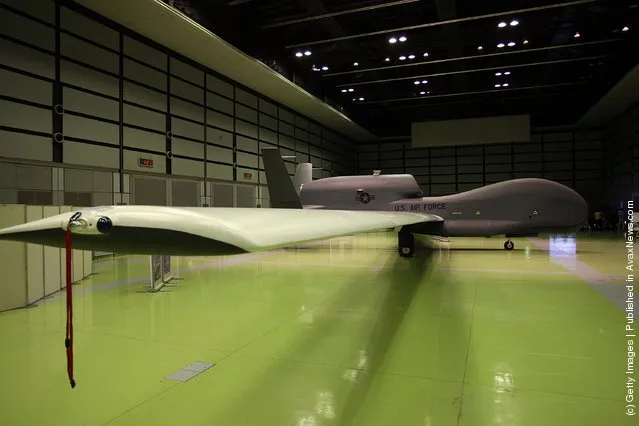
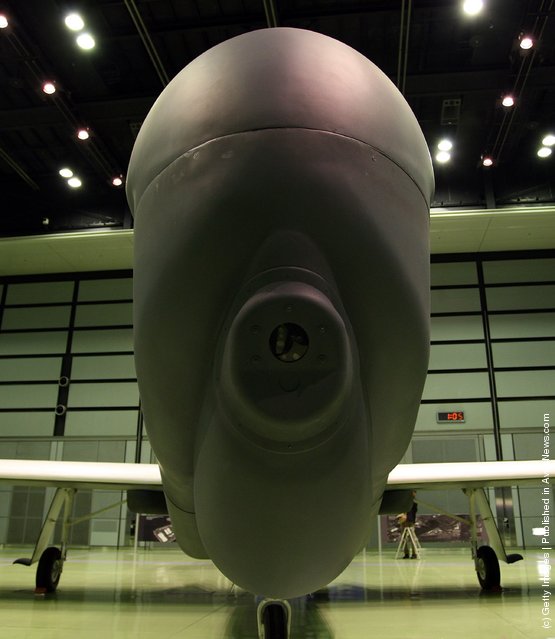
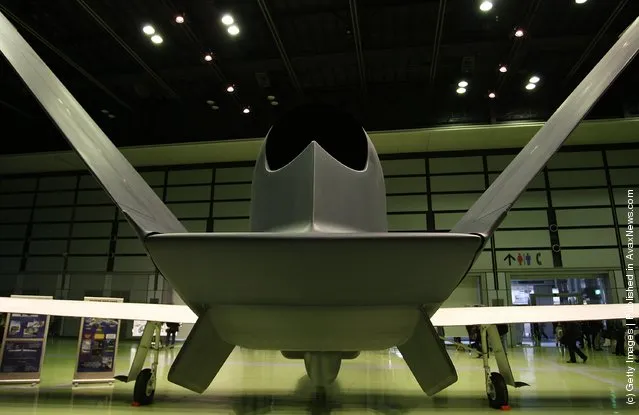
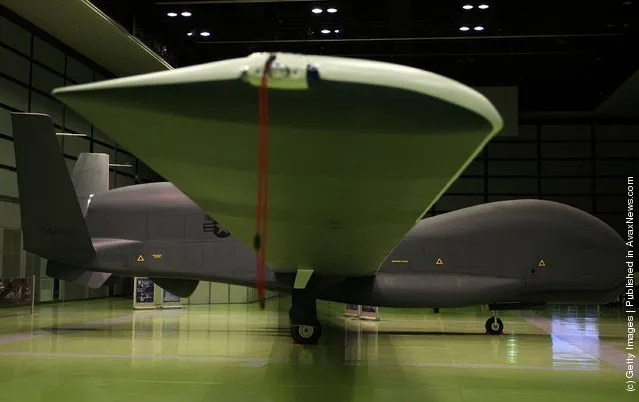
“The Northrop Grumman (formerly Ryan Aeronautical) RQ-4 Global Hawk (known as Tier II+ during development) is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) used by the United States Air Force and Navy as a surveillance aircraft.
In role and operational design, the Global Hawk is similar to the Lockheed U-2, the venerable 1950s spy plane. It is a theater commander's asset to provide a broad overview and systematic target surveillance. For this purpose, the Global Hawk is able to provide high resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) — that can penetrate cloud-cover and sandstorms — and Electro-Optical/Infrared (EO/IR) imagery at long range with long loiter times over target areas. It can survey as much as 40,000 square miles (103,600 square kilometers) of terrain a day.
The Global Hawk costs about $35 million USD (actual per-aircraft costs; with development costs also included, the per-aircraft cost rises to $123.2 million USD each).
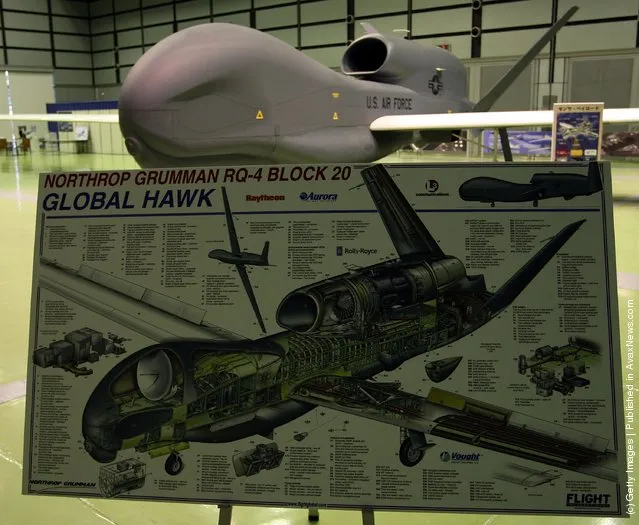
The Global Hawk carries the “Hughes Integrated Surveillance & Reconnaissance (HISAR)” sensor system. HISAR is a lower-cost derivative of the ASARS-2 package that Hughes developed for the Lockheed U-2. HISAR is also fitted in the US Army's RC-7B Airborne Reconnaissance Low Multifunction (ARLM) manned surveillance aircraft, and is being sold on the international market. HISAR integrates a SAR-MTI system, along with an optical and an infrared imager. All three sensors are controlled and their outputs filtered by a common processor. The digital sensor data can be transmitted at up to 50 Mbit/s to a ground station in real time, either directly or through a communications satellite link”. – Wikipedia
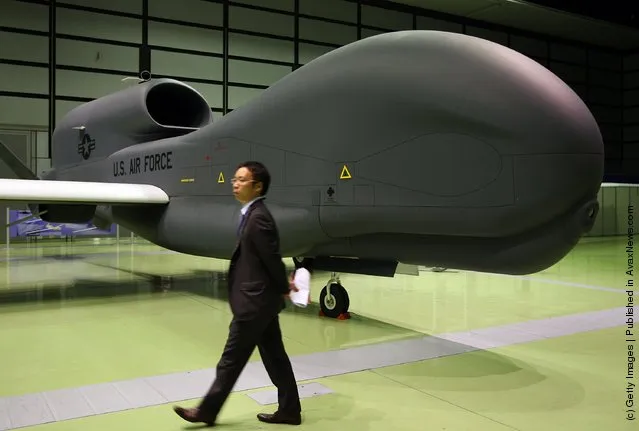
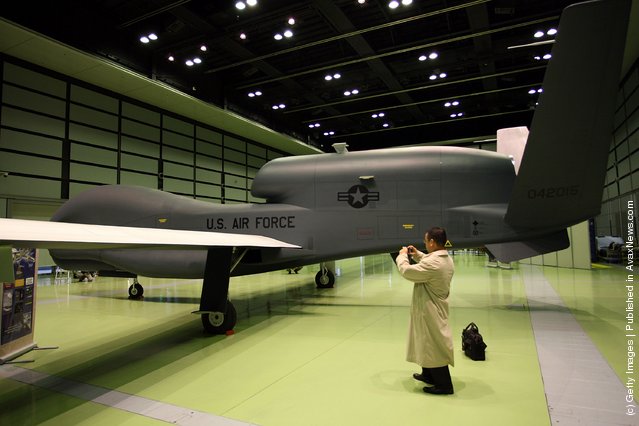
Photos: A full-scale model of The RQ-4 Global Hawk unmanned plane is displayed during a presentation at PiO Exhibition Center on March 24, 2010 in Tokyo, Japan. (Photo by Koichi Kamoshida/Getty Images)
In role and operational design, the Global Hawk is similar to the Lockheed U-2, the venerable 1950s spy plane. It is a theater commander's asset to provide a broad overview and systematic target surveillance. For this purpose, the Global Hawk is able to provide high resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) — that can penetrate cloud-cover and sandstorms — and Electro-Optical/Infrared (EO/IR) imagery at long range with long loiter times over target areas. It can survey as much as 40,000 square miles (103,600 square kilometers) of terrain a day.
The Global Hawk costs about $35 million USD (actual per-aircraft costs; with development costs also included, the per-aircraft cost rises to $123.2 million USD each).
The Global Hawk carries the “Hughes Integrated Surveillance & Reconnaissance (HISAR)” sensor system. HISAR is a lower-cost derivative of the ASARS-2 package that Hughes developed for the Lockheed U-2. HISAR is also fitted in the US Army's RC-7B Airborne Reconnaissance Low Multifunction (ARLM) manned surveillance aircraft, and is being sold on the international market. HISAR integrates a SAR-MTI system, along with an optical and an infrared imager. All three sensors are controlled and their outputs filtered by a common processor. The digital sensor data can be transmitted at up to 50 Mbit/s to a ground station in real time, either directly or through a communications satellite link”. – Wikipedia
Photos: A full-scale model of The RQ-4 Global Hawk unmanned plane is displayed during a presentation at PiO Exhibition Center on March 24, 2010 in Tokyo, Japan. (Photo by Koichi Kamoshida/Getty Images)









23 Jul 2011 12:31:00,
post received
0 comments