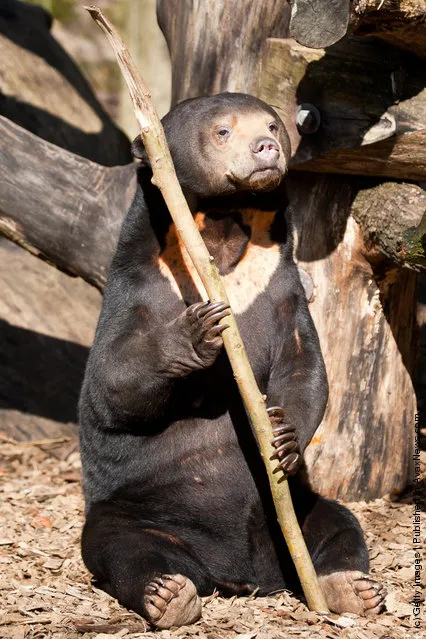
The sun bear (Ursus malayanus), also known as the honey bear, is a bear found primarily in the tropical rainforest (the dense lowland forests) in Southeast Asia; North-East India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Southern China, Peninsular Malaysia, and the islands of Sumatra and Borneo.
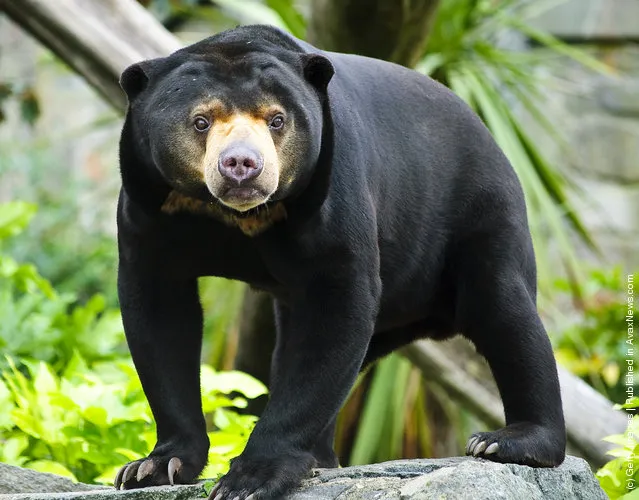

The sun bear does not hibernate, and, as a result, it can reproduce year-round. The offspring reach sexual maturity after 3–4 years and may live up to 30 years in captivity. A female sun bear can produce 1 to 2 cubs per year. Sun bears undergo a roughly 96 day gestation period after which the 300 to 400 g cub is born blind and hairless. The cub is initially totally dependent on its mother and suckling can continue for about 18 months. After 1 to 3 months, the young cub can run, play and forage near its mother. Male sun bears grow larger than females. Females are observed to mate at about 3 years. During time of mating, the sun bear will show behaviour like hugging, mock fighting and head bobbing with its mate.
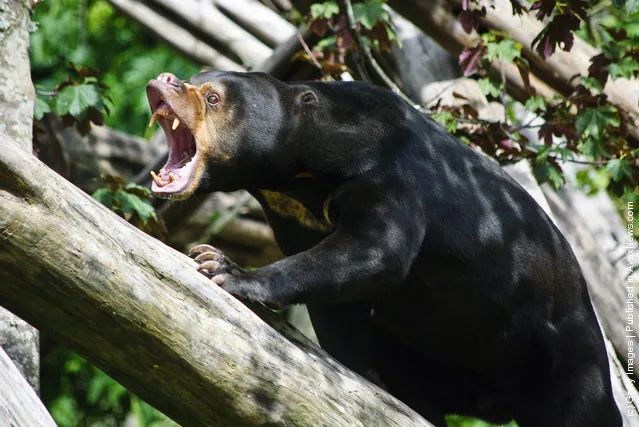

Adult sun bears have few predators except humans, due to their fierce reputation and formidable teeth. Occasionally, they may be overwhelmed by tigers, or large reticulated pythons. Other possible predators include the leopard, the clouded leopard, and the sun bear's larger sympatric relative, the Asiatic black bear. The bear's loose skin on its neck allows it to wriggle its body inside its skin far enough to turn around and bite its attacker when grabbed.
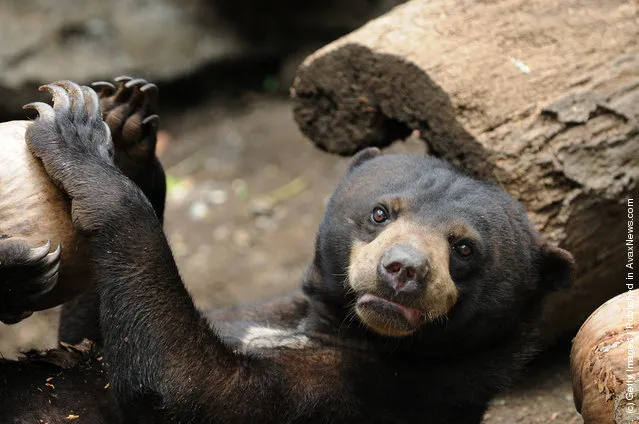
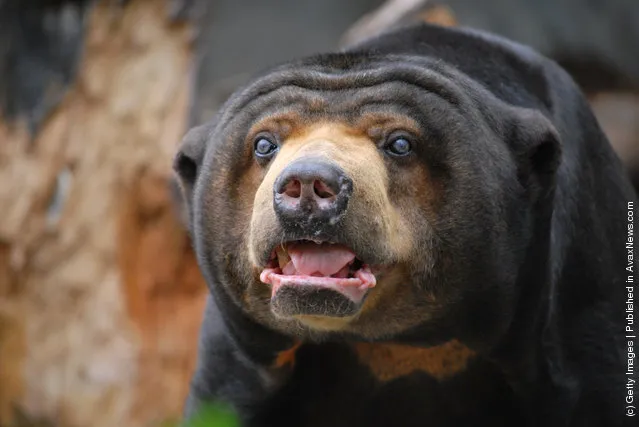
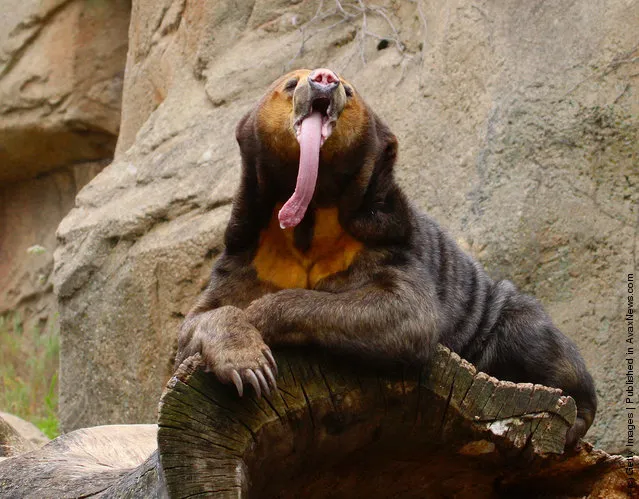



The diet of the sun bear consists mainly of invertebrates and fruits but as omnivores they will eat a wide variety of foods including small vertebrates, such as lizards, birds, and turtles, eggs, the young tips of palm trees, nests of bees, berries, sprouts, roots, and coconuts. In fact, sun bears have been observed to eat over 100 insect species and over 50 plant species.
Despite being able to eat many leaves, the sun bear has certain favourite food sources. This was demonstrated in a study where termites, ants, beetles and beetle larvae made up the majority of the invertebrates eaten, whilst figs were the most important fruit source consumed. They eat termites by thrusting their paws into termite mounds and licking them off their paws.
The sun bear's fondness for honey gives rise to its alternative name of the 'honey bear'. In Malay and Indonesian, it is known as 'Beruang Madu' which translates to honey bear.
Its powerful jaws can crack open nuts. Its long, powerful claws are used to break into tree trunks and fallen logs to access honey, grubs and termites. Much of the sun bear's food must be detected using its keen sense of smell, as its sight is poor.
Despite being able to eat many leaves, the sun bear has certain favourite food sources. This was demonstrated in a study where termites, ants, beetles and beetle larvae made up the majority of the invertebrates eaten, whilst figs were the most important fruit source consumed. They eat termites by thrusting their paws into termite mounds and licking them off their paws.
The sun bear's fondness for honey gives rise to its alternative name of the 'honey bear'. In Malay and Indonesian, it is known as 'Beruang Madu' which translates to honey bear.
Its powerful jaws can crack open nuts. Its long, powerful claws are used to break into tree trunks and fallen logs to access honey, grubs and termites. Much of the sun bear's food must be detected using its keen sense of smell, as its sight is poor.
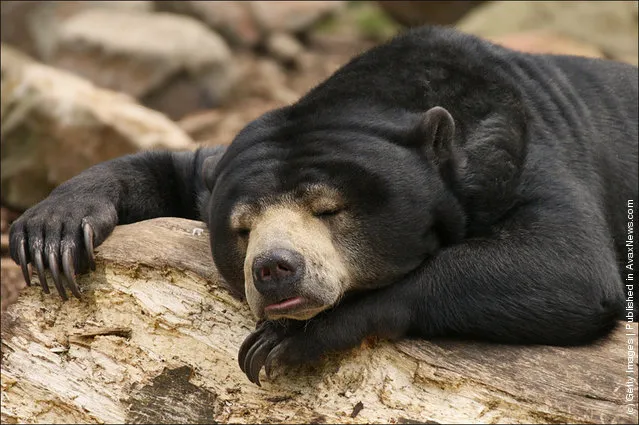

Being a primarily nocturnal creature, the sun bear tends to rest during the day on lower limbs not far above the ground. Because it spends so much time in trees, the sun bear can sometimes cause damage to property. It has been known to destroy coconut palms and cacao trees on plantations.

via flick/wikipedia
03 May 2012 23:37:00,
post received
0 comments