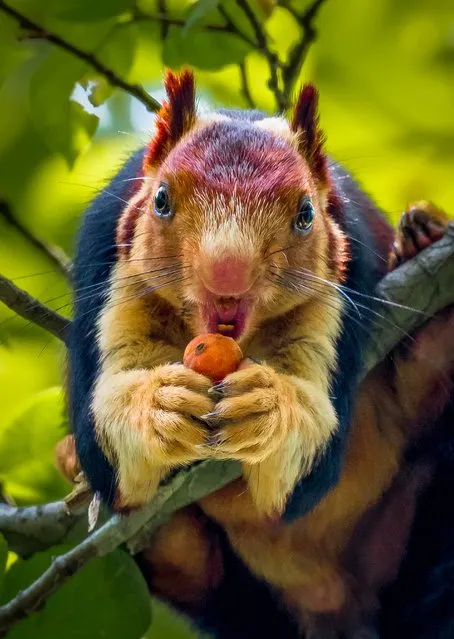
The Malabar Giant squirrel – double the size of their grey relatives and measuring up to 36 inches (91.5 cm) from head to tail – lives deep in the forests of India. The athletic animals can leap an incredible 20 feet (6 m) between trees. Photographer Kaushik Vijayan, 39, snapped the animals in their native habit to produce these stunning images. Kaushik, from Kerala State, India, said: “Up until that point I had never heard about a squirrel like that or seen one. The sight was an absolute feast for my eyes. The squirrels fascinated me and I got excited to capture this beauty on my camera”. (Photo by Kaushik Vijayan/South West News Service)
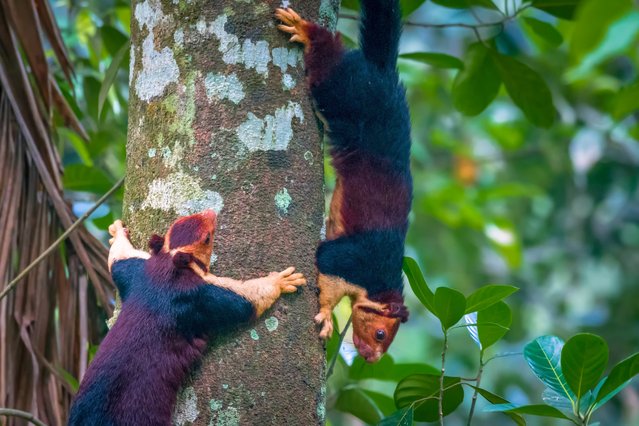

The Indian giant squirrel, or Malabar giant squirrel (Ratufa indica) has a conspicuous two-toned (and sometimes three-toned) color scheme. The colors involved can be creamy-beige, buff, tan, rust, brown, or even a dark seal brown. The underparts and the front legs are usually cream colored, the head can be brown or beige, however there is a distinctive white spot between the ears. Adult head and body length varies around 14 inches (36 cm) and the tail length is approximately 2 ft (0.61 m). Adult weight – 2 kg (4.41 lb). (Photo by Kaushik Vijayan/South West News Service)
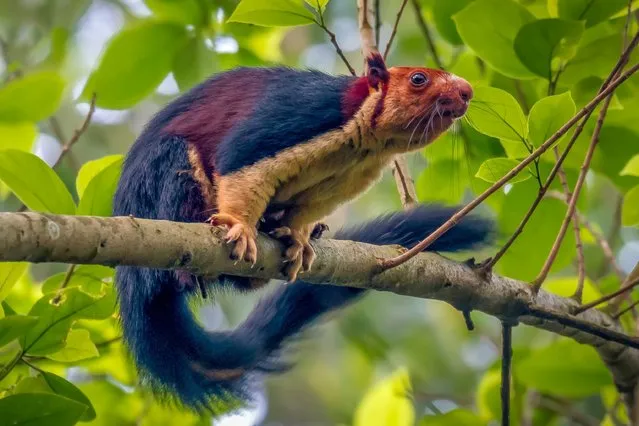

Malabar giant squirrels feeding on a ripe jackfruit. (Photo by Kaushik Vijayan/South West News Service)
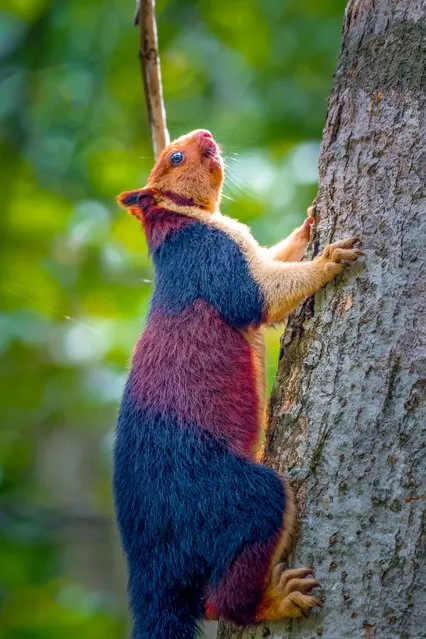

The Indian giant squirrel is an upper-canopy dwelling species, which rarely leaves the trees, and requires “tall profusely branched trees for the construction of nests”. It travels from tree to tree with jumps of up to 6 m (20 ft). When in danger, the Ratufa indica often freezes or flattens itself against the tree trunk, instead of fleeing. (Photo by Kaushik Vijayan/South West News Service)
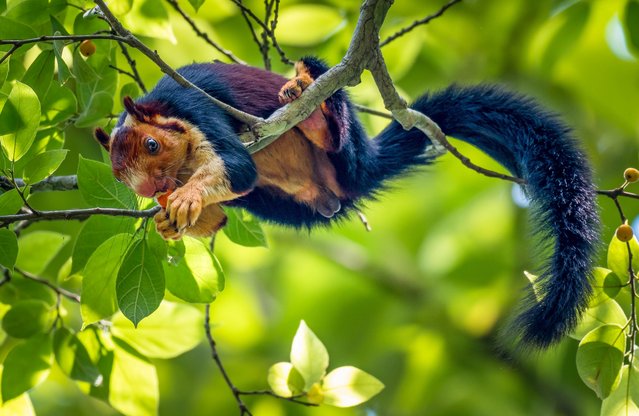

Its main predators are the birds of prey and the leopard. The Giant Squirrel is mostly active in the early hours of the morning and in the evening, resting in the midday. They are typically solitary animals that only come together for breeding. (Photo by Kaushik Vijayan/South West News Service)

The species is believed to play a substantial role in shaping the ecosystem of its habitat by engaging in seed dispersal. Diet includes fruit, flowers, nuts and tree bark. Some subspecies are omnivorous, also eating insects and bird eggs. (Photo by Kaushik Vijayan/South West News Service)
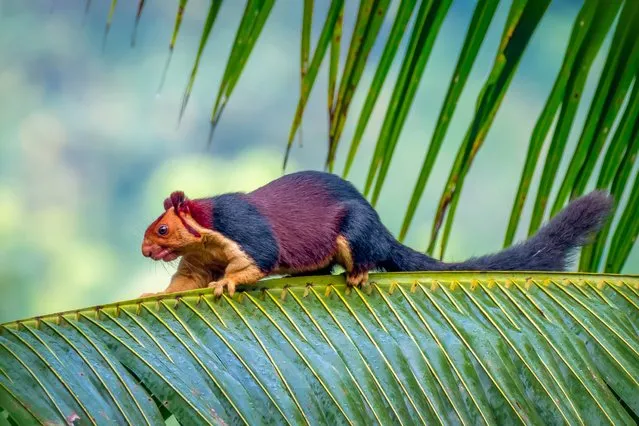

The Indian Giant Squirrel lives alone or in pairs. They build large globular nests of twigs and leaves, placing them on thinner branches where large predators can't get to them. The species is endemic to deciduous, mixed deciduous, and moist evergreen forests of peninsular India, reaching as far north as the Satpura hill range of Madhya Pradesh (approx. 22° N). (Photo by Kaushik Vijayan/South West News Service)
04 Apr 2019 00:03:00,
post received
0 comments