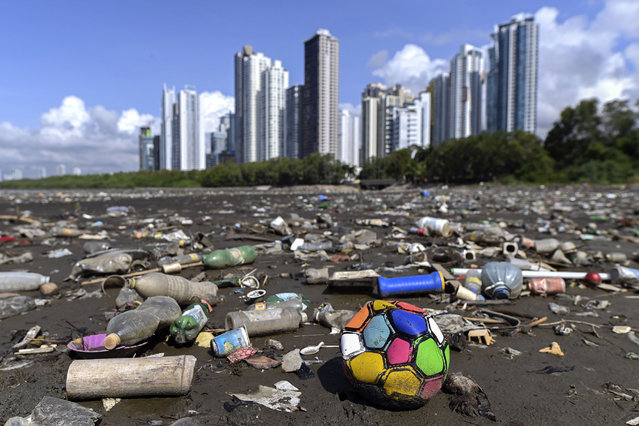
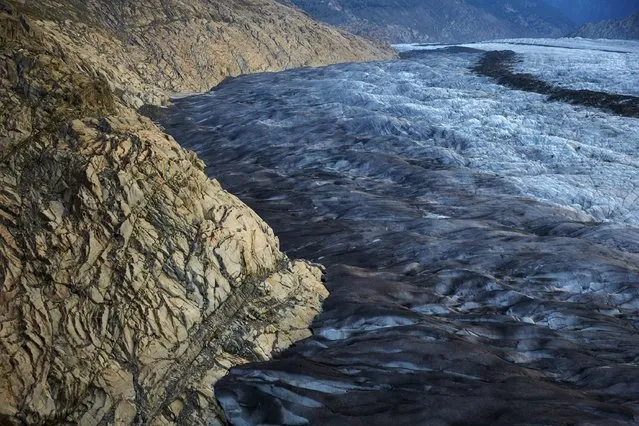
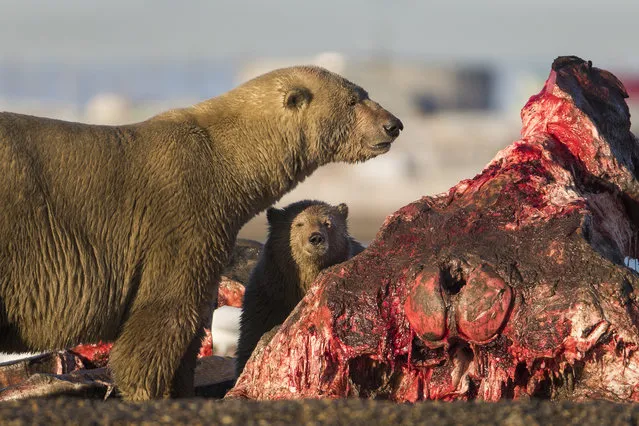
Garbage, including plastic waste, is seen at the beach of Costa del Este, in Panama City, on April 19, 2021. Every two weeks, Marine Biology students descend about five meters in the sea to take care of a coral nursery of the staghorn species (Acropora cervicornis) in Portobelo, Panama, with which they aim to restore reefs damaged by climate change and pollution, as part of the Reef2Reef project. (Photo by Luis Acosta/AFP Photo)
21 Jun 2021 07:30:00,post received
0 comments