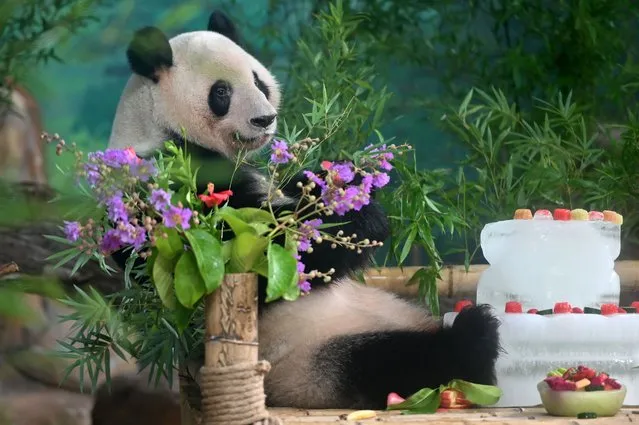
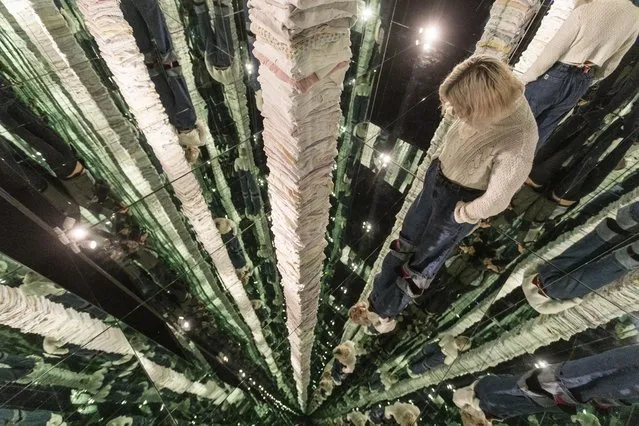
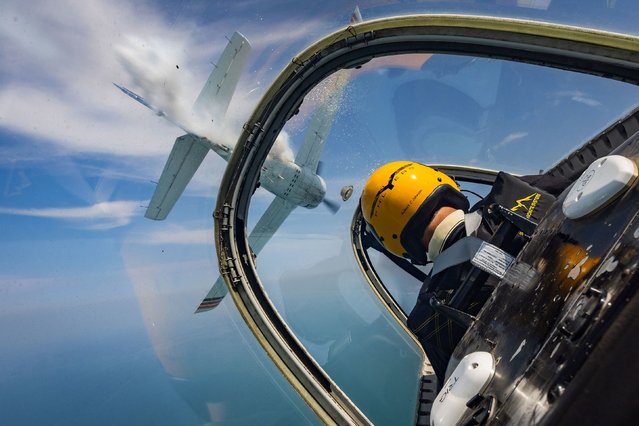
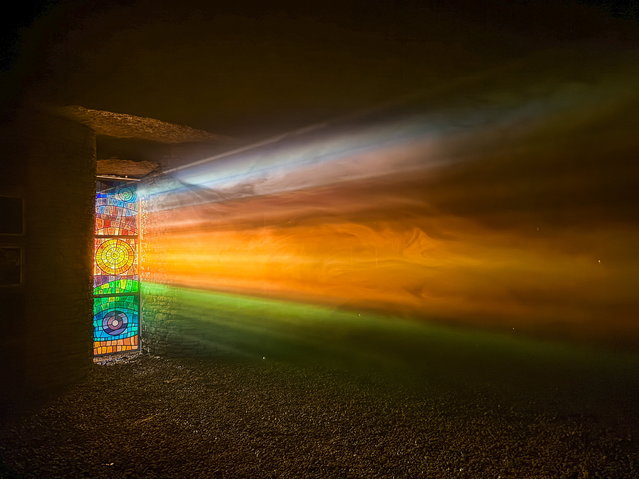
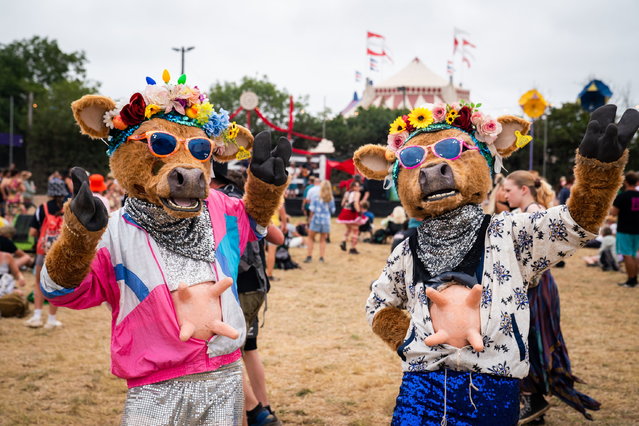
Giant panda Ji Lan enjoys an iced birthday cake at Nanning Zoo on June 27, 2022 in Nanning, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of China. Giant panda Ji Lan and her brother Ji Mei celebrated their sixth birthday on Monday in Nanning. (Photo by Yu Jing/China News Service via Getty Images)
04 Jul 2022 04:33:00,post received
0 comments