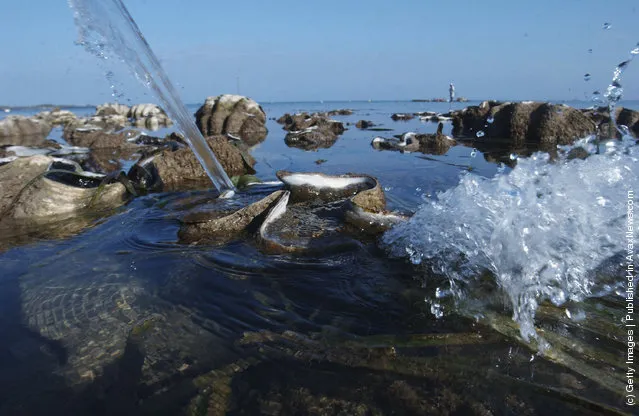
“The giant clam, Tridacna gigas (known as pā’ua in Cook Islands Māori), is the largest living bivalve mollusc. T. gigas is one of the most endangered clam species. It was mentioned as early as 1825 in scientific reports. One of a number of large clam species native to the shallow coral reefs of the South Pacific and Indian oceans, they can weigh more than 200 kilograms (440 lb) measure as much as 120 cm (47 in) across, and have an average lifespan in the wild of 100 years or more”. – Wikipedia
Photo: Tridacna Gigas, or Giant Clams spew water as a traditional fisherman passes by a small sanctuary on January 23, 2004 near Bolinao in the Northern Philippines. The clams, prime builders for coral reefs and providing shelter for spawning fish and other marine life, are exposed by low tides in the sanctuary. Overfishing and pollution throughout the country are not only threatening food security, but are also starting to choke one of the few working clam sanctuaries in the world. (Photo by David Greedy/Getty Images)
Photo: Tridacna Gigas, or Giant Clams spew water as a traditional fisherman passes by a small sanctuary on January 23, 2004 near Bolinao in the Northern Philippines. The clams, prime builders for coral reefs and providing shelter for spawning fish and other marine life, are exposed by low tides in the sanctuary. Overfishing and pollution throughout the country are not only threatening food security, but are also starting to choke one of the few working clam sanctuaries in the world. (Photo by David Greedy/Getty Images)
01 Oct 2011 13:10:00,post received
0 comments