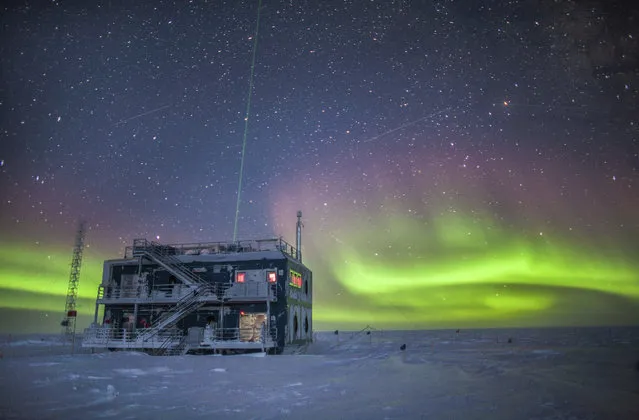
This undated photo provided by NOAA in May 2018 shows aurora australis near the South Pole Atmospheric Research Observatory in Antarctica. When a hole in the ozone formed over Antarctica, countries around the world in 1987 agreed to phase out several types of ozone-depleting chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Production was banned, emissions fell and the hole shriveled. But according to a study released on Wednesday, May 16, 2018, scientists say since 2013, there’s more of a banned CFC going into the atmosphere. (Photo by Patrick Cullis/NOAA via AP Photo)
15 Aug 2018 00:05:00,post received
0 comments