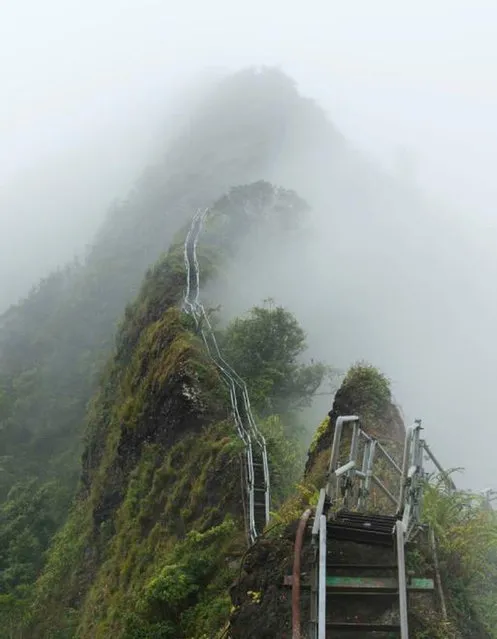
The Haʻikū Stairs, also known as the Stairway to Heaven or Haʻikū Ladder, is a steep hiking trail on the island of Oʻahu. The trail began as a wooden ladder spiked to the cliff on the south side of the Haʻikū Valley. It was installed in 1942 to enable antenna cables to be strung from one side of the cliffs above Haʻikū Valley to the other. A building to provide a continuous communication link between Wahiawā and Haʻikū Valley Naval Radio Station was constructed at the peak of Puʻukeahiakahoe, elevation about 2,800 feet (850 m). The antennae transmitted very low frequency radio signals from a 200,000-watt Alexanderson alternator in the center of Haʻikū valley. The signals could reach US Navy submarines as far away as Tokyo Bay while the submarines were submerged.