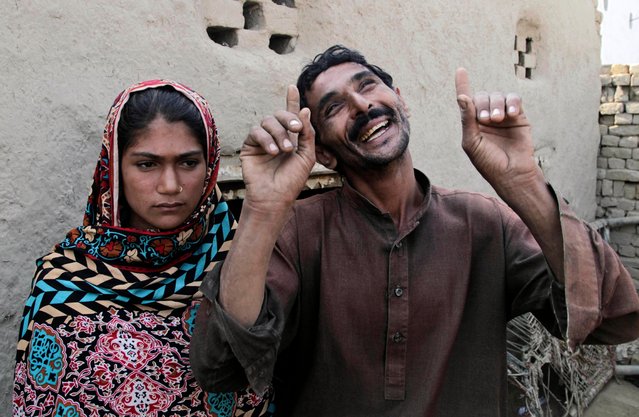
In this Tuesday, December 20, 2016 photo, Mohammad Ramzan, right, reacts while talking to The Associated Press with his young bride Saima in Jampur, Pakistan. Saima was given as a bride to the older man by her father so he could marry the groom’s sister, a practice of exchanging girls that is entrenched in conservative regions of Pakistan. It even has its own name in Urdu: Watta Satta, “give and take”. A mix of interests – family obligations, desire for sons, a wish to hand off a girl to a husband – can lead to a young teen in an a marriage she never sought. (Photo by K.M. Chaudhry/AP Photo)
31 Dec 2016 10:08:00,post received
0 comments